Grab the modern dental services
We provide quality services
Focuses on improving the appearance of teeth, gums, and smile. Includes procedures like whitening, veneers, bonding, and contouring. Often uses advanced materials for natural-looking results. May also have functional benefits. Increasingly popular due to demand for a better smile.
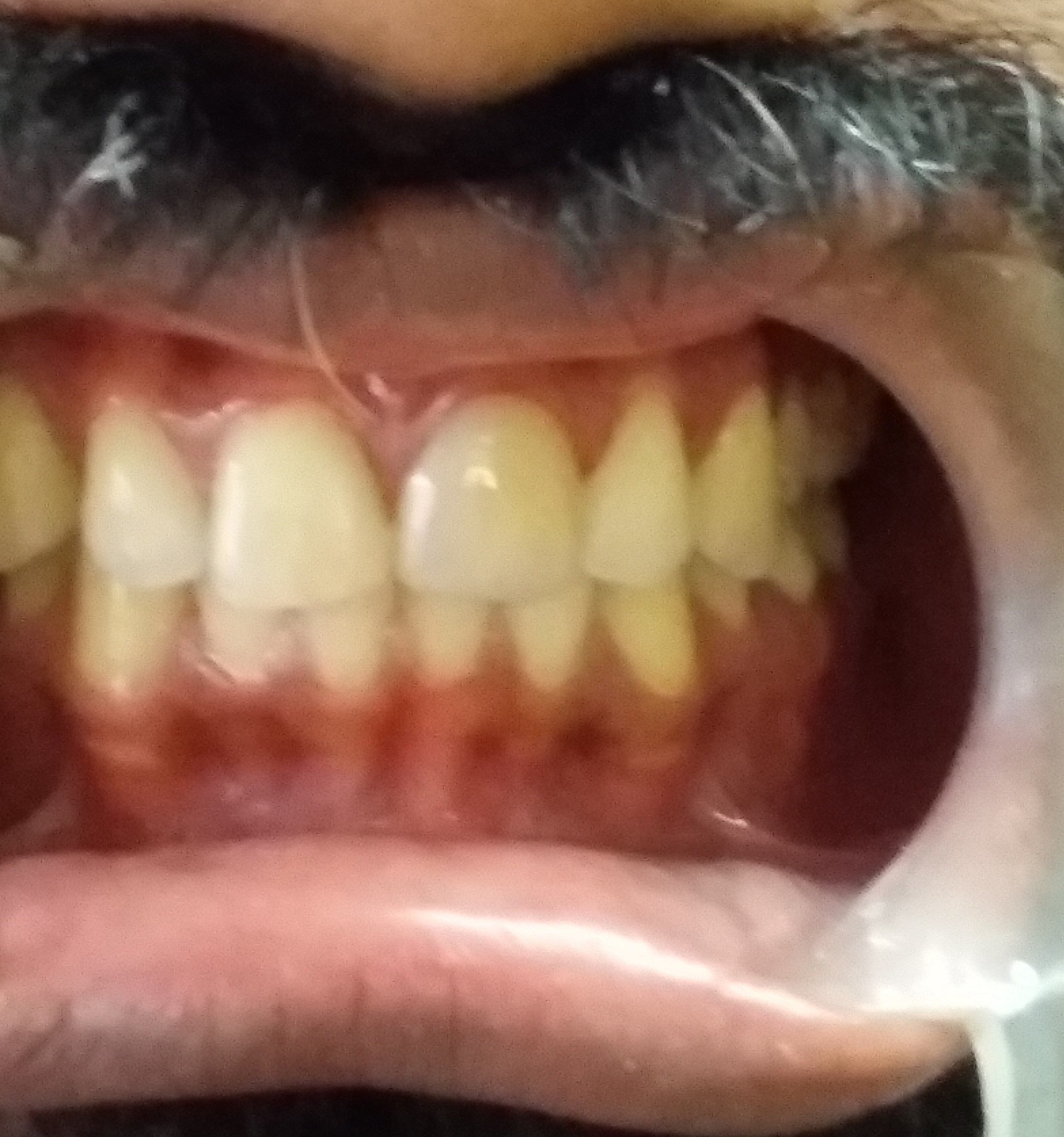 Before: The individual needed correction of a discoloured tooth and closure of spacing between teeth.
Before: The individual needed correction of a discoloured tooth and closure of spacing between teeth.
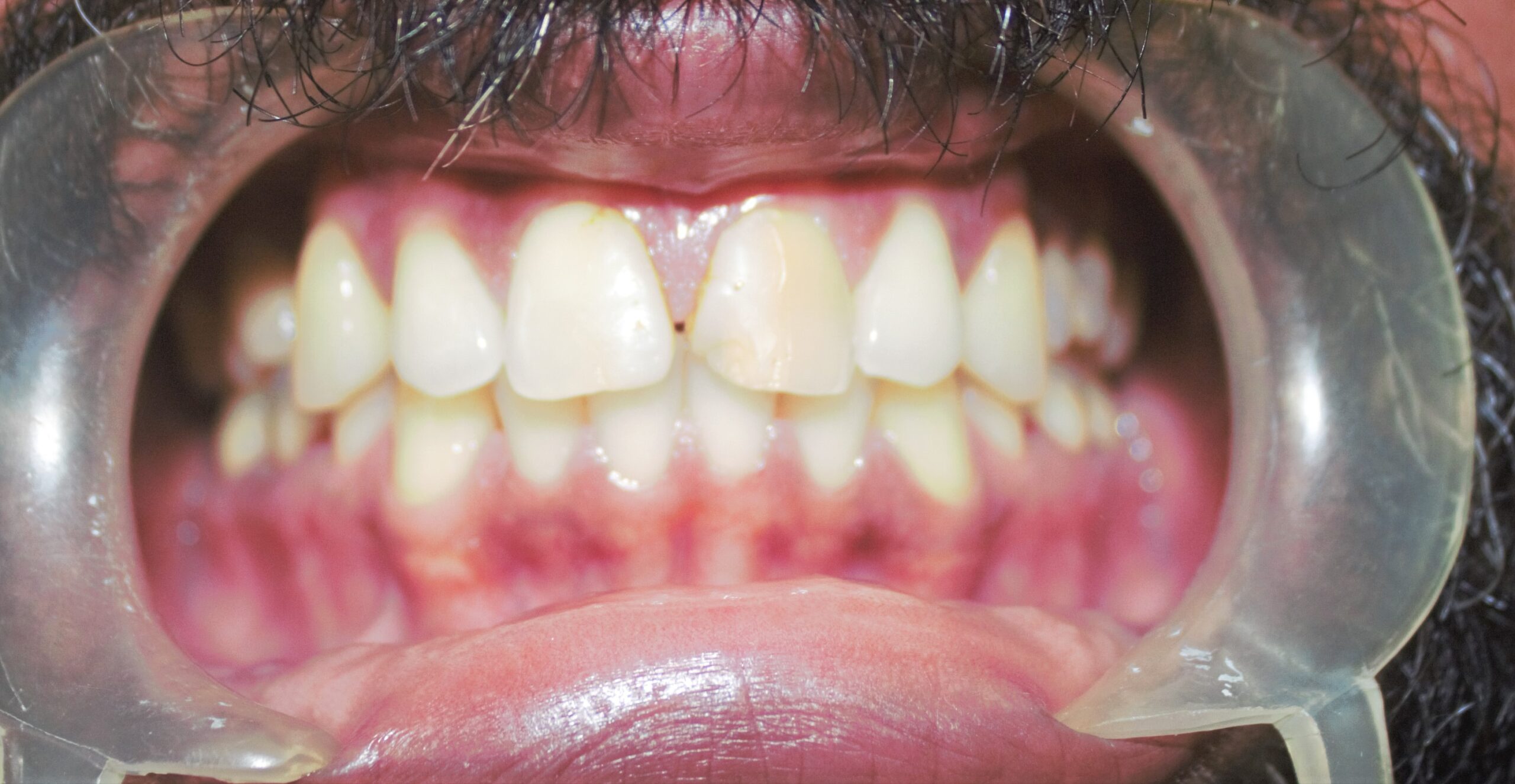 After: The individual needed correction of a discoloured tooth and closure of spacing between teeth.
After: The individual needed correction of a discoloured tooth and closure of spacing between teeth.
Improvements in materials and techniques for adhesive Dentistry, has given the restorative Dentist the option for treatment which are more conservative and aesthetic than before. One of the important developments is Cosmetic dentistry in the last of twentieth century was the development of dental Veneers especially ceramic veneers.
Veneers can be made by using Dental composite (tooth coloured filling material) which can made directly on the tooth or indirectly where it is fabricated outside on models as ceramic veneers, and placed on to the tooth using a bonding agent and resin glu
The disadvantage of composite dental veneers is that, they get easily dislodged when involving the incisal tip of the tooth but of the dental veneers are kept away from the insisal tip of the tooth, their chances of success is high and the added advantage of composite dental veneer is that they can be repaired easily by the application of dental composites.
Ceramic veneers
They are made from a shell of tooth, (ceramic) which covers the labial as well as the incisal area (insiso They are -lingual ) like a butt joint.
The advantage of dental ceramic veneers is that less tooth reduction is needed compared to a dental crown. Much stronger than a dental composite veneers, which can facture easily, but if the dental ceramic veneer is subjected to excessive clenching or compression forces it can facture or cleaves away from the tooth.
Though there are advantages and disadvantages of dental ceramic and dental composite veneers depending on the aesthetic needs, area of tooth which needs replacement or correction dental composites or dental ceramics can be the material of choice of the treatment for dental veneers.
Metal free ceramic crowns
Metal free ceramic crowns one of the most aesthetic dental crowns in the market, where instead of a metal substructure, a ceramic batching is used as the base of ceramic, it has the advantage that it doesn’t from a black line along the gum margin, due to the corrosion of metal backing along the cervical margins of the metal ceramic crowns.
But metal free ceramic crowns has the disadvantage that they fracture easily when masticatory forceses are exerted on them.
Provided gum recessions, which can form due to age, improper maintenance of oral care along the gum margins of the dental crowns are also seen in metal free ceramic crowns also.
Metal ceramic crowns
Ceramic fused to metal has the strength of metal and aesthetes of ceramics ceramic fused to metal restorations has an initial coping which fits over the stump, over which ceramic is added. The metal coping will be a thin layer at the gingival margin, and certain times a small part of the metal is removed and instead ceramic is added over that area.
Metal ceramic crown has three layers, an opaque porcelain to mask the opaque colour of metal body porcelain and incisal porcelain.
One of the major reasons for acceptance of ceramic fused to metal crown, was due to the strength of metal and its ability to bond to the ceramic metal.
But one of the major disadvantages of metal ceramic crown was the formation of a black line along the cervical margin due to the exposure of the metal to oral fluids and formation of corrosion products this affecting the aesthetic appearance of the crown.
Addresses the dental needs of older adults. Manages issues like dry mouth, tooth loss, and gum disease. Emphasizes prevention and coordination with medical care. Promotes comfort and oral function in elderly patients. Supports improved quality of life for aging populations.
Old age brings us a lot of health problems and the commonly seen dental problems in old age include cavities and gum problems. The problem is aggravated by medical condition such as dry mouth, which due to the side effect of medications taken for systemic medical health problems.
Dry mouth can be avoided by
Using oral moisturiers, such as mouth wash.
Drinking plenty of water, even if not thirsty\
Using sugar free gums to stumilate salavial production.
Avoid food and beverages which can cause iritation to oral mucosal tissues.
Consult a Dentist and get flouride varnish to protect the teeth from cavities.
Gum disease
Many older adults have gum and periodontal problems which is due to plaque which irritate the gums and make then swollen, red and which makes them bleed.
One difficulty of gum problem is that it is a painless condition until to the advanced stage. If they are left untreated the gums detach from the teeth and leads to plaque and food accumulation and eventually damage to the supporting structures of the tooth and loss of tooth itself.
Prevention of gum problems
Prevention of calculas by proper brushing technique using interdental brushes, and oral irrigators which helps to flush out lodged food debris between tooth and thus prevent gum inflammation.
Root carries
Another common problem see is root caries, which is caused by lodgement of food inter-proximally and which if not removed will end up in root caries.
Natural tooth can last decades or even your entire life, it they are cared for properly, provided natural tooth can be retained by preventive Dentistry, restorative Dentisty, or even through root canal treatment with a dental crown and at certain times by a dental post.
Advantaged or retaining natural tooth
The function of your smile will be much better with natural tooth, than artificial (prosthetic) tooth. Even through dental bridges and implants can give a good appearance some thing that is natural cannot be replaced by artificial means. Provided there is no difficulty as such of removable dentures, which has to cleaned for removal and even kept out of the oval cavity during night. Retention of natrual teeth is cheap in the long run. A mouth without tooth is like a mill without a blades natural tooth are precious and should be lead to preserved at any cost, by the various treatment modalities which are available for us in the Dental fraternity.
Specializes in restoring and replacing missing or damaged teeth. Involves crowns, bridges, dentures, and implants. Aims to restore function, aesthetics, and oral health. Handles complex reconstructive cases. Often works with other dental specialists for full-mouth rehabilitation.
Missing tooth replacement is a necessity, especially the anterior, front tooth. But it is equally important in the posterior region also.
It is thought in mind that, Dental arch is statistic entity, but certianly it is not the situation. The maxillary and mandibular teeth are in dynamic equilibrium, where they support each other. When tooth is lost, the structural integrity of the arch is lost and the tooth realigns to the new occlusion. Provided teeth adjacent to it may drift bodily, or even tilt, opposing teeth may erupt into the extraction space.
Such drifted and supra-erupted tooth can result in food impaction and eventually proximal caries, And even plaque accumulation and periodontal breakdown and loss of tooth.
Contact and contours are an important part of crowns, these contacts and contours act as spill way for food and prevent food passage into sublingual area.
The contact area proximally on molar tooth is located to the occlusal third, except for the second molar, which is located to middle third. The contact area should be than just a point and is normally an area. The area cervical to contact area should be flat or concave and never should be convex, since that can course gingival inflammation. The proximal contacts are slightly facial to the contour except for the maxillary 1st and 2nd molar which is pretty centralilised. If the contact area is to narrow, it can act as a area of food wedging especially for fibrous foods, and if the contact area is too wide facio-lingually, they do not deflect food from gingival tissues.
The height of contour or the facial surfaces of all posterior tooth occurs in the cervical third and similar in the lingual surfaces of maxillary premolars and maxiillary molars.On mandibular tooth on the lingual side, this height of contour occur in the middle third.
The amount of lingual curvature varies from 0.5mm on maxillary molars and mandibular 1st premolars and 0.75mm on mandibular 2nd premolars. It is 1mm on mandibular molars. The contours of tooth play on important role because over contouring of tooth can cause food accumulation on cervical area and gingival inflammation.Thus the importance of proper contours in crown is mandatory for preventing food impaction and food accumulation and thus promoting good gingival health.
Deals with diseases of the dental pulp and root tissues. Main procedure is root canal treatment. Saves infected teeth and relieves pain. Uses advanced tools and techniques for precise care. Prevents tooth loss and maintains oral health.
Root canal treatment is done on tooth, when the pulp of the tooth is involved by dental caries
When we critically analyse the situation the tooth root has a middle third and apical third, The middle third of the tooth may be of various thickness, certain times they are narrow and at certain times broad.
When we look at the apical third, it may be broad apically, or some times narrow apically, and at certain times curvatures at the apical third.
Along with it. changes occur in the tooth (pulp) chamber, especially clacifications, pulp stones. Hyper cementosis, in the apical l third.
These are all the situations which come to our day to day practice in Endodontics and which can hinder the success of the root canal treatment.
A root canal treatment is a successful treatment if the Dentist is able to manage all these situations successfully to the apical third.Provided proper of root canal preparation and proper protocol of root canal sealers as followed.
Failure of a root canal can be due to problems of improper preparation of the root canal space,(shaping and cleaning) which includes the middle third as well as apical third of the root canal space. Provided a good post-Endodontic restoration such as a crown, should be clearly done, without any open margins.
Root canal treatment is successful treatment, provided it has to be done with proper treatment protocol and which cannot be imparted forcefully to do it properly, and can be mastered with proper interest and training. Provided it is difficult to re-correct a improperly done root canal.
A peri apical lesion of dental origin can be due to a long standing chronic caries, history of trauma on tooth and improperly done root canal treatment.
Earlier peri apical lesions where managed by apicectomy (surgical removal of the apical third and a retrograde filling) which used to get dislodged and happen to get re infected. With the advent of better techniques in root canal treatment, the management of such tooth became easier and were successful with predictable results.
Such involved tooth where managed non surgically by re-root canal treatment, and where followed by x-rays in a period of three months, six months, and one year.Large cyst of Endodontic origin where managed by removal of the cyst, than apicectomy (where the apical third of the tooth where surgically removed)
With the introduction of newer instrumentation techniques and instruments and epoxy resin and bio ceramic root canal sealers, the need for apicectomy was avoided with proper root canal and re-root canal treatment being carried out with ease.
Provides dental care to children from infancy to adolescence. Includes preventive care, fillings, and early orthodontic assessments. Trains in behavior management and child-friendly treatment. Educates parents on dental hygiene. Builds positive dental habits early in life.
The surface of the tooth, especially molars and pre molars have small depressions called as pits, which act as an area for food lodgement and thus initiation of decay can result. Children at small age, when the first permanent molar erupt into the oral cavity, doesn’t know how to brush properly decay would have started in the permanent molars.
In such a tooth, pit and fissure sealants should be applied for the prevention of caries. These pit and fissure sealants help in preventing food lodging on the released surface of tooth where these pits and fissures are mainly founds.
Sealants should be placed on all permanent tooth especially molars without cavitations after eruption of the tooth. Sealants should be placed on primary molars of children who are prone for caries Resin based sealers should be used, than glass ionomer sealers. Sealants should not be placed in decayed a partly erupted tooth.
Application procedure
The tooth surface should be cleaned of any calculus and cleaned with pumice before application of etchant, washed out and dried, followed by the application of bonding agent, light curing it and application of pit and fissure sealants and light activating it.
An application of pit and fissure sealants will normally last for maximum of one year, by the time it will wear out due to masticatory load. Pit and fissure sealants should be applied till the age of twelve years, and can be stopped even before that, if the child learns to brush properly by himself or herself.
Application of pit and fissure sealants is helpful in prevention of cares especially in young children, and should be carried out as a routine procedure.
Oral habits in children is a concern for Dentist, as well as the paediatrician, speech therapist and parent. Regarding the dentist part the habits such as thumb sucking, tongue thrusting can result in the changes of the alveolar ridge, potential problems in position of teeth and development of malocclusion which can be due to prolonging of abnormal habits.
The problem is that the Dentist rarely sees the child earlier and only by the time the habit has established and damage to the teeth in the form of malocclusion of teeth. Tongue thrusting is defined as a human behavioural pattern where the tongue protrudes through the anterior tooth during speech and swallowing.
Thumb sucking is a procedure where the thumb is inserted into the mouth and where a pleasure is obtained for the individual, Both these habits can lead to dexterous effect in the oral cavity if the habit pursuit beyond the exception of the permanent teeth.
Tongue thrusting can be due to hyper plastic tonsils, prolonged thumb sucking, nasal congestion, macroglossia and secondary to early extraction of deciduous tooth and an anterior open bite.
Treatment of Thumb sucking and tongue thrusting
The treatment of tongue thrusting primarily involves, the correction of cause, once the cause is corrected, the tongue musculature can be controlled by muscle retaining an exercise technique, which redirects the muscle associated with swallowing.
Mechanical restraining method where an appliance is placed in the mouth which will restrain the tongue and thus preventing it pushing forwards wing mechanical retainers such as cribs.
While thumb sucking is performed for oral satisfaction, serve thumb sucking can lead to proclamation of maxillary anteriors, constriction of the maxilla, retroclination of lower actions and an increased over jest and open bite. Usually following the thumb sucking, tongue thrusting can develop as secondary.
Corrects misaligned teeth and jaws using braces, aligners, and other devices. Improves bite, speech, and dental health. Treats crowding, spacing, and jaw irregularities. Often begins in childhood or early teens. Enhances smile and self-confidence.
Focuses on gum and supporting bone health. Treats gum disease with cleaning, scaling, surgery, and maintenance. Plays a key role in preventing tooth loss. Supports implant procedures and gum aesthetics. Essential for long-term oral health.
A caries in a tooth can lead to pulpal infection and even peri-apical leshion of the tooth. To save a tooth is our primary aim, and we should take necessary steps to save a tooth, than removal of a tooth by surgical removal.
A tooth pulp can get infected by dental caries, or even by periodontal involvement. Endodontic and periodontic leshions can happen together with the tooth getting infected. In a tooth there are accessory canals, the apical foramen and the dentinal tubuules of tooth can get expressed due to root planning procedures.
In such mobile tooth which are of periodontal orgin, due to the presence of calculus and microorganisms affect the supportive structures of tooth, the periodontal ligament and finally through apical foramen, the infection reaches the pulp of tooth.
In such situations the treatment of choice root canal treatment followed by periodontal surgery.
Our mouth is full of bacteria, which along with the food debris and other substances form a colourless sticky layer on tooth called as plaque which can be removed by brushing and flossing. Once it hardens it is called as plaque, which can be removed by a Dental professional only. The longer the plaque and tartar are on the tooth, more troublesome it becomes. The bacteria in the tartar cause gum inflammation, which is seen as gum swelling and bleeding. This form of gum disease can be reverted back by proper oral prophylaxis by a dentist, and regular brushing and flossing which can prevent bone loss and periodontal tissue breakdown.
When gingivitis is left untreated it spreads to periodontitis due to the damage caused to the supporting structures of the tooth, by the bacterial toxics which are produced by the plaque bacteria and also assisted by the inflammatory responses of the body mechanism, which eventually damage the supporting structures of the gingival tissue and the alveolar bone. If left untreated it can end up in loss of the tooth.
Treatment plan
Periodontitis can be diagnosed by clinical examination using a periodontal probe and by radiographic examinination of bone loss. Periodontitis are painless and will be noted at a later stage only if individual is careless.
Preventive measures
Proper brushing twice a day, such a way that the bacterial plaque is disrupted and proper flossing daily.
Preserves natural teeth with minimal intervention. Treats cavities and damage with fillings, inlays, and sealants. Prioritizes early detection and treatment. Uses aesthetic materials for natural results. Helps avoid more invasive procedures.
An excellent contact is that one, that provides a natural look and feel reproducing natural contacts or even improving them. The contact is located in the occlusal and middle third of most tooth, thus providing and embrasure for food passage.
A proper contact helps prevent for wedging between teeth, help distribute the masticatory load on the teeth, thus preventing the excess load on the tooth and supporting structures.
Spaces between the contact area causing food wedging can cause periodontal inflammation, mobility of tooth and halitosis. Alternatively the shape of the col (interdental space) is also determined by the proper contact area.
To achieve proper contact and contour of a restoration is a necessity of any class II dental restoration, which ever material is used for dental restoration (composite a amalgam) Proper contact and contours can be achieved by a toffel mayor retainer or using a sectional matrix such as palodent.
This dental restorations which are carved to proper contact and contours play a vital role in the maintaining proper health of the periodontium of the tooth, which ever material (Dental Amalgam or Dental Composite is used as restorative material of choice for restoration.
Dental Composites
A new era in Dental restorative materials began in 1955 when Bunocre found that acrylic resin formed acceptable micro mechanical adhesion with dry dental canal that had been etched with phosphoric acid.
Most Dental restorative resin systems are based on UDMA or BISGMA materials, with an added filler particles, which determines the final property of the composite which include the shade opacites, translucency and polish ability of the composites. When the flow of composite increases, the amount of filler particle is reduced, such composites have the disadvantage that the co-efficient of thermal expansion is more, leading to micro leakage and secondary caries, along restoration margins.
Hybrid are a combination of micro fills and larger filter particles sizes the disadvantage is the inability to polish.
Presently Nano hybrid Dental composites are the dental composites in the market, the choice of dental composites. Tooth coloured filling material should be decided by physical properties, amount of filler particles and size of filler particular, which decides the polish ability of the dental composite.
Advantages – of composites include esthetics, which is one of the prime factor of composite restorations. Less tooth reduction when compared to amalgam restoration and it is insulative in nature and are added advantage is that it can be repaired when fracture of restoration occurs.
Disadvantages
The major disadvantage of composite is the shrinkage of composite, which is decided by two factors.
The quality of Bond
The shape of cavity
The shape of the cavity effect in shrinkage of dental composite depends on the ratio of the bonded to unbounded surface of the preparation. The stress on the restoration increases, as the amount of bonded surface increases a class I restoration has five bonded and as unbonded surface.
Taking into consideration of biocompatibility matter of dental composites, they cannot be placed in deep cavity directly, such deep cavities should be protected with a insulate barrier such as glass ionomer to protect pulp tissue. For a successful composite restoration, adequate time should be spent, curing each increment, provided a properly functioning light unit should be used and light guide should be as close as possible and at right angles to the material being photo curved.
Dental Amalgam
Dental amalgam is an alloy of silver tin, and small amounts of copper to which mercury is added. Depending on the amount of copper added it can be divided into high copper and low copper amalgam. High copper amalgam has better corrosion resistance than low copper amalgam.
Depending an particle size Dental amalgam can be classified as i) Spherical or (ii) spheroid.
Depending on Presence of copper (i) high copper are (ii) low copper
Amalgam has its properties such as excellent compressive strength, but once the dental restoration of amalgam factures due to occlusal load, correction of such a filling is difficult and the whole filling should be replaced.
Dental composites or Dental amalgam has its our merits and disadvantages but at the end of the day the individual wants a filling which is stable and with out causing him any pain.
Replaces missing teeth with surgically placed implants. Implants support crowns, bridges, or dentures. Offers a durable and natural-feeling solution. Requires careful planning and bone evaluation. Restores chewing, speech, and confidence.
End-osseus Dental implants have a become a significant factor in Prosthetic and Restorative Dentistry since 1970’s
In spite of the advances in techniques, materials and implants design, implant failure is still a concern for the dental profession.
The success of the implant depends or the
- Site of the implant
- Patient factors
- Implant factors
- Skill of the surgeon
- It should be differentiated between implant failure, due to loss of osteointergration, fracture of abutment, or even loosening of the abutment, which can be due to excessive load exerted on the implant.
One of the early pioneers in the field of dental implant, Schroeder and followed by work of Branenmark who found the single tooth root implant.
At present success rate of dental implant (endosseous) ranges from 85% for fixed Prosthodontics and 98% and higher for single tooth implants.
Success of dental implants depends on primarily by absence of pain and rigid fixation of dental implants. Others say bone loss less than 1/3rd the crestal height of the alveolar bone.
Probing depth less than 6mm, a minimal bleeding index, less than two weeks of per implantitis and no radiolucency in adjacent bone.
Success for an implant
Patient factors
Bone quality is important in the success of the implant. Bone quality can be divided into
Type1
Homogenous compact bone, throughout the entire jaw.
Type 2
Core of dense trabecular bone; surrounded by compact bone of cortical plate.
Type 3
Dense trabecular bone, with thin cortical bone.
Type 4
low density trabecular bone with a thin cortical bone.
(Type 1 ) and (type 2) ideal for implants.
Systematic Diseases
Diabetes -High uncontrolled diabetes can affect the blood supply of the bone thus chances of implant rejection is high.
Osteoporosis
Can affect the intergrity of the implant
Irradiated Jaw,reduced blood supply, osteoradio necrosis
xerostomia which are seen in radiation therapy can affect the implant. Ideally it is good to wait for 6-12 months before placing implant.
Infection
Infection at the site can be a reason for implant failure which should be looked into before implant is placed.
Oral leshions can be a reason for implant failure.
Inproper oral hygiene
Plaque accumulation leads to inflammation and eventually leads to periodontitis and implant failure.
Age and sex
Has a role in implant failure since as we age the bone healing ability is reduced.
Oral Habbits
Smoking and bruxism can affect the intergrity of the dental implants. During bruxism, horizontal forceses are exerted on the dental implants, which can cause excessive osteoclastic activity at the site of implant and no osteo blastic activity at the region.
So in an implant the forceses should be transmitted through the long axis of the implant. In bruxers by reducing the surface area of the crown, and also by increasing the length and width of dental implant effect of bruxism can be reduced.
Site selection
The importance of site comes to play in bone quantity, quality and forceses of mastication the bone is subjected to, and close proximity to Endodontic restorations, which helps the Dentist to go far an implant, or avoid an implant. If going for an implant, the length and width of the implant choosen matters in bone selection.
Bone augmentation or bone grafting which needs to be done in certain situations, can be a failure in the situations like osteoporosis periodontial disease or even infection which can affect the integrity of bone formation.
Provided the timing of the placement of the implant in the grafted bone is important, time should be given for the grafted bone to mature and usually it takes 6-12 months for lamellar bone, which can adhere to implant interface.
Bone grafting can be successful procedure, provided adequate blood supply to the area and micro movement of the implant doesn’t occur during the osteointegration stage.
Occlusal Forceses
Implants being ostio intergrated with bone doesnt have periodontal support as natural tooth, so shear forces are damaging to the implant. The implant and corresponding tooth should be designed in such a way that forces should be directed along the long axis of the implant, such a way that shear forceses are prevented from acting on the cervical margin of the tooth, especially on the buccal side of the implant. Forceses along the long axis of the implant are well tolerated, but shear forces not good, it can lead to bone loss on cervical area. Sites which are more posterior are subjected to more occlussal forces since they are close to the fulcrum of the mandible.
Implant Design (Factors)
Length of implant
Average length of the implant used varies from 10-16mm, longer implant better bone contact which improves the stability of the implant to occlusal forces.
Width of the implant
Increase in width of the implant with grooves in the implant make the surface area contacted by the implant increases, which increases the stability of implant to occlusal forceses
A healthy gingival sulcus of 3-4mm should maintained between the implant and crest of the alveolar bone.
An implant placed next to a tooth should be at least 3 mm apart so as the provide adequate blood supply to the periodontal ligament. Implant to implant should be placed 4-7mm, to prevent bone necrotic and thus failure of implant.
Surgical Technique
When bone is exposed to temperature of (470C) for more than 1 minute, it results in collagen damage, bone necrosis and eventually death of bone, which results in collagen adhering to implant and bone, than proper osteo integration.
This can happen when excessive pressure and excessive speed is applied during the drilling procedure of the implant, insufficient coolant is used during the drilling procedure far implant. Using a surgical length no. 2 round bur, the density and thickness of the bone can be evaluated.
Time of implant loading
Implant should be loaded depending on the density of the bone, from a period of four months to one year. Early loading can affect osteo- integration along the implant and finally the implant can end up in failure due to fibrous collagen formation between the implant and bone. Occlussion should be adjusted such a way that excessive forcesses should not be directed on the implant which can effect the ostiointegration of the implant. Provided the oral hygeine of the individual can affect the life of the implant, due to improper plaque removal and not using interdental cleansing aids, which can cause gum inflammation.

